SAE J2735-Draft-Rev28 [issued: 11-10-08]
-
265 -
This is an SAE Motor Vehicle Council draft document of the DSRC committee, subject to change.
Annex C-6 Stop Sign Movement Assistance
Application Description
This application provides a warning to a vehicle that is about to cross through an intersection after having
stopped at a stop sign. This may prevent collisions with traffic approaching the intersection. In particular,
this application warns drivers when a collision is probable if the indicated start-from-stop is initiated.
Flow of Events
Flow of events
1.
Vehicle “A”, starting from stop, sends MSG_BasicSafetyMessageFrame, Part I
2.
Vehicle “B” receives message
3.
Vehicle “B” recognizes that Vehicle A’s message is relevant and, per the message
information (e.g. location, speed, heading, acceleration, throttle position, etc.), that
trajectories of Vehicles “A” and “B” will likely intersect.
4.
Vehicle “B” alerts its driver to a straight crossing path hazard.
5.
Vehicle “B” sends MSG_BasicSafetyMessageFrame, Part I
5.
Vehicle “A” receives message.
6.
Vehicle “A” process the message from Vehicle A and determines that Vehicle B’s message
is relevant (crossing road segment via map and/or heading)
7.
Vehicle “A” alerts its driver to a start-from-stop hazard.
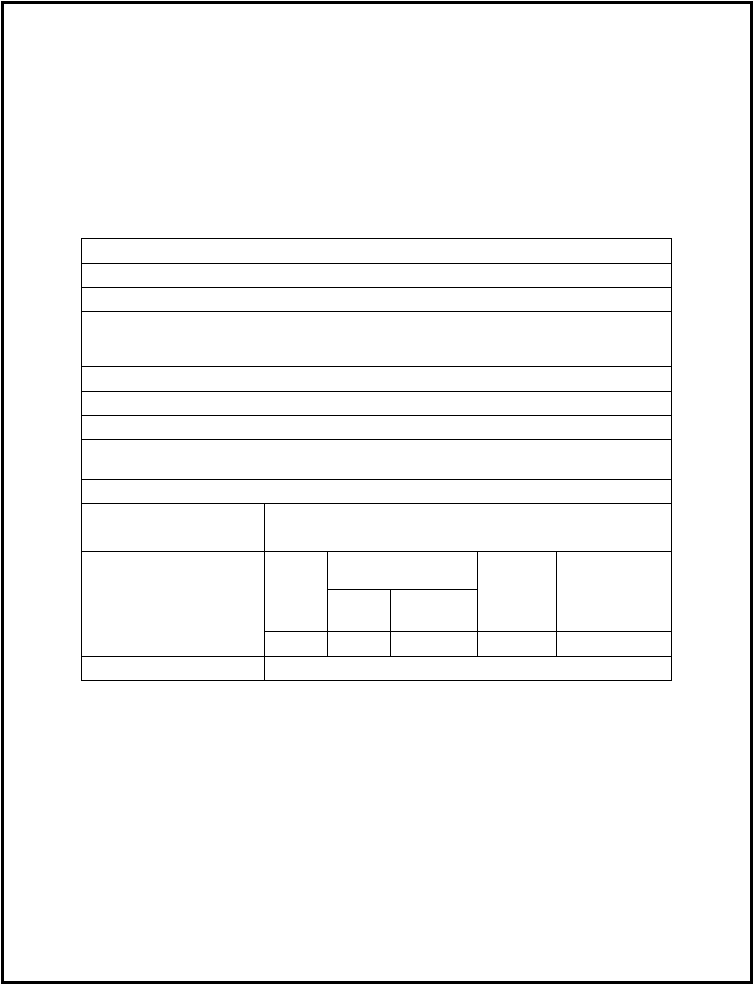
Hardware Devices:
DSRC radio
Positional and vehicle sensors
Human-Machine Interface
Occupant
Vehicle
System
Driver
Passenger
Service
Provider
Road
Department
Actors: (What entities play an
active role in use)
X
X
Support information:
CAMP-VSC Task 3 Report, 2003
Concept of Operations
DSRC communications is used to allow the stopped vehicle to be informed of the presence of other
vehicles in the immediate vicinity. The frequently broadcast MSG_BasicSafetyMessageFrame, Part I and
MSG_BasicSafetyMessageFrame, Part II messages from vehicles in the area allow the stopped vehicle to
receive the position, velocity, acceleration, and control parameters, among others, from these vehicles. The
in-vehicle unit, based upon the host vehicle’s stopped condition and combination of release of brake and
application of throttle, for example, constructs a predicted travel path for the host vehicle and also
constructs expected travel path for the other detected vehicles by analyzing their received parameters. If the
in-vehicle unit determines that a collision would be likely if the start-from-stop maneuver is initiated, an
appropriate warning is issued to the driver.

